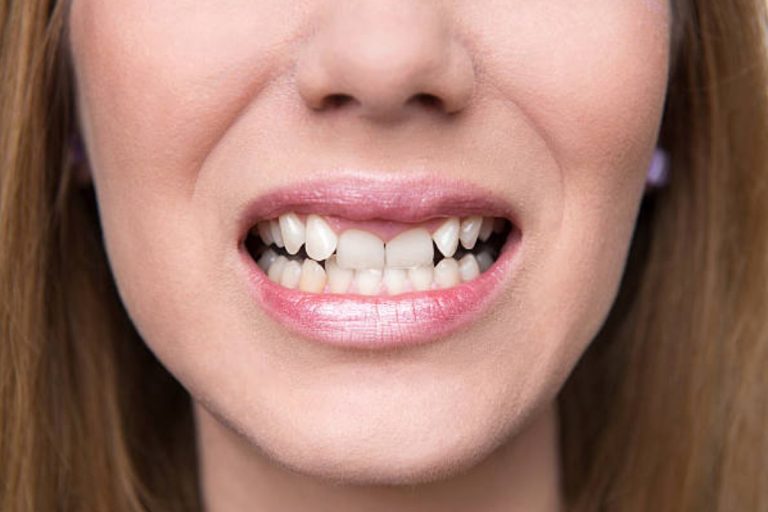
Buck teeth, or protruding or prominent front teeth, refer to a dental condition where the upper front teeth stick out farther than usual. This condition can affect children and adults, causing various functional and aesthetic concerns.
Buck teeth may result from genetic factors, habits like thumb-sucking, or other underlying dental issues.
In this outline, we will explore the causes of buck teeth, their effects on an individual’s life, available treatment options, preventive measures, and the importance of seeking professional help.
Additionally, we’ll touch upon the psychological and emotional impact of buck teeth and the support available for individuals dealing with this condition.
By addressing buck teeth, individuals can improve their oral health, enhance their self-esteem, and minimize potential difficulties related to speech, eating, and overall well-being.
Definition of buck teeth
Buck teeth, medically known as a dental protrusion or overjet, is a dental condition characterized by the upper front teeth extending forward and protruding beyond the lower front teeth while the mouth is closed.
This increases the horizontal gap between the upper and lower teeth, creating an overbite.
The excessive prominence of the upper front teeth gives the appearance of “buck teeth,” often causing aesthetic concerns for individuals.
Buck teeth can vary in severity, ranging from a slight overjet to a more pronounced protrusion. The condition can affect both children and adults.
It may cause by genetic factors, developmental issues, habits like thumb-sucking or pacifier use, tongue thrusting, jaw misalignment, or specific injuries or traumas.
Common causes of buck teeth
Common causes of buck teeth include:
- Genetics: Inherited factors play a significant role in dental development, including the positioning and alignment of teeth. Certain genetic traits can contribute to the likelihood of developing buck teeth.
- Habits: Prolonged thumb-sucking, pacifier use, or other oral habits can pressure the developing teeth and jaw, leading to the protrusion of the upper front teeth over time.
- Tongue Thrusting: Tongue thrusting refers to pushing the tongue against the front teeth during swallowing or at rest. This repeated pressure can cause the upper front teeth to move forward, resulting in buck teeth.
- Jaw Misalignment: Problems with the alignment of the upper and lower jaws can contribute to buck teeth. If the upper jaw protrudes or the lower jaw set back, it can create an overjet, causing the upper front teeth to stick out.
- Delayed Tooth Eruption or Early Tooth Loss: When primary (baby) teeth are lost prematurely, or permanent teeth are slow to erupt, it can disrupt the natural progression of dental alignment. This may lead to irregularities, including buck teeth.
- Trauma or Injury: Accidents or injuries to the mouth or jaw can cause misalignment or displacement of the teeth. If not properly treated, these conditions can result in buck teeth.
It’s important to note that multiple factors can contribute to the development of buck teeth, and it’s often a combination of these causes that leads to the condition.
Consulting with an orthodontist or dentist can help determine the underlying causes and guide appropriate treatment options.
Importance of addressing buck teeth
Addressing buck teeth is essential for several reasons:
- Aesthetics and Self-Esteem: Buck teeth can significantly impact an individual’s appearance and self-confidence. The protrusion of the upper front teeth may cause self-consciousness and lead to a negative self-image. By addressing buck teeth, individuals can improve the alignment of their teeth, enhance their smile, and boost their self-esteem.
- Dental Function: Buck teeth can affect the proper functioning of the teeth and jaws. Misaligned teeth may result in difficulties with chewing and biting, which can impact overall nutrition and digestion. Correcting buck teeth can help improve dental function, making eating, speaking clearly, and maintaining oral hygiene easier.
- Speech and Articulation: The position of the teeth plays a crucial role in speech production. Buck teeth can affect the pronunciation of certain sounds and words, leading to speech difficulties or lisping. Individuals can improve their speech clarity and communication skills by aligning their teeth properly.
- Oral Health: Buck teeth can increase the risk of oral health problems. The protruding upper front teeth may be more susceptible to trauma, tooth decay, and gum disease. Misaligned teeth can also make oral hygiene practices, such as brushing and flossing, more challenging. Correcting buck teeth can help reduce the risk of dental issues and maintain better oral health.
- Long-Term Stability: Addressing buck teeth improves immediate concerns and contributes to long-term dental stability. Proper teeth alignment allows for a balanced bite, reducing the strain on individual teeth and jaw joints. This can help prevent future dental problems, such as excessive wear, jaw pain, and temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders.
- Overall Well-Being: The physical and psychological impact of buck teeth can affect an individual’s well-being. By addressing this condition, individuals can experience improved confidence, enhanced social interactions, and better overall quality of life.
It’s essential to consult an experienced dentist or orthodontist to determine the most suitable treatment options for buck teeth.
Early intervention often recommended to prevent further complications and achieve optimal results.
Causes of Buck Teeth
Genetics
Genetics plays a significant role in the development of buck teeth. Certain inherited traits can influence teeth’ position, size, and alignment, including the likelihood of developing dental protrusion.
If a person has family members with buck teeth or other orthodontic issues, they may be more prone to developing the condition themselves.
Genetic factors can affect the growth and development of the jaw bones, tooth size, and the relationship between the upper and lower jaws.
Variations in genes responsible for dental development can contribute to malocclusions, including buck teeth.
It’s important to note that genetics alone may not be the sole cause of buck teeth.
Other factors include buck teeth, thumb-sucking, tongue thrusting, or jaw misalignment.
Understanding the genetic component of buck teeth can help determine the appropriate treatment approach.
Orthodontic interventions, such as braces or aligners, can help guide the teeth into proper alignment and overcome genetic tendencies.
By addressing the genetic factors through orthodontic treatment, individuals can achieve a healthier, more aligned smile and reduce the impact of buck teeth on their oral health and overall well-being.
Consulting with a dental professional, such as an orthodontist, can comprehensively assess the genetic and environmental factors contributing to buck teeth and guide personalized treatment options.
Thumb-sucking or pacifier use
Thumb-sucking or pacifier use is a common habit among infants and young children. While it can provide comfort and help with self-soothing, prolonged thumb-sucking or pacifier use can contribute to the development of buck teeth. Here’s how:
- Pressure on Teeth and Jaw: The continuous sucking motion exerts pressure on the developing teeth and jaw. Over time, this pressure can cause the upper front teeth to push forward, creating an overjet or dental protrusion.
- Altered Oral Habits: Thumb-sucking or pacifier use can disrupt the natural positioning of the tongue and interfere with proper oral muscle development. Improper tongue posture or abnormal swallowing patterns can further contribute to the misalignment of teeth, including buck teeth.
- Duration and Intensity: The duration and intensity of thumb-sucking or pacifier use play a role in its effect on dental development. Prolonged and vigorous sucking habits increase the likelihood of dental problems, including buck teeth.
It’s worth noting that not all children who engage in thumb-sucking or pacifier use will develop buck teeth.
The impact of these habits varies depending on factors such as the duration, intensity, and individual susceptibility to dental changes.
However, to prevent buck teeth, it is recommended to:
- Encourage the Discontinuation of the Habit: Gradually wean infants and young children off thumb-sucking or pacifier use as they age. Positive reinforcement, rewards, or distraction techniques can help break the habit.
- Use Behavioral Strategies: Using finger guards, bitter-tasting nail polish, or thumb-sucking deterrents can discourage children from continuing the habit.
- Provide Alternative Coping Mechanisms: Offer alternative comforting techniques or toys to replace thumb-sucking or pacifier use, redirecting the child’s attention and soothing needs.
If the habit persists or has caused noticeable dental changes, seeking guidance from a dentist or orthodontist is crucial.
They can assess the extent of the dental protrusion and recommend appropriate orthodontic interventions, such as braces or aligners, to correct the buck teeth and properly align the teeth and jaws.
Early intervention is vital in addressing the effects of thumb-sucking or pacifier use on dental development.
Taking proactive measures and seeking professional guidance minimizes these habits’ impact on buck teeth’ growth, leading to improved oral health and aesthetics.
Tongue thrusting
Tongue thrusting refers to a habit where the tongue pushes against the front teeth during swallowing, at rest, or during speech. This repetitive force against the teeth can contribute to the development of buck teeth. Here’s how tongue thrusting can affect dental alignment:
- Pressure on Teeth: The constant pressure exerted by the tongue against the front teeth can push them forward over time. This can lead to an overjet or protrusion of the upper front teeth, resulting in buck teeth.
- Abnormal Swallowing Pattern: Tongue thrusting often accompanies an irregular swallowing pattern called “tongue thrust swallow.” Instead of placing the tongue against the palate during swallowing, individuals with tongue thrusting tend to push their tongue against the front teeth. This further reinforces the pressure on the teeth and contributes to misalignment.
- Impaired Resting Position: Tongue thrusting can affect the resting position of the tongue. Rather than resting against the roof of the mouth, the tongue may rest low in the mouth, allowing the upper front teeth to protrude. This can influence the positioning and alignment of the teeth over time.
Various factors, including anatomical issues, allergies, airway problems, or certain oral habits, can influence tongue thrusting habits.
It is essential to address tongue thrusting to prevent or correct the development of buck teeth. Treatment options may include:
- Orofacial Myofunctional Therapy focuses on retraining the tongue and orofacial muscles to establish proper swallowing patterns and resting positions. Exercises and techniques promote tongue posture and strengthen the correct muscles.
- Orthodontic Treatment: In cases where tongue thrusting has caused significant dental protrusion, orthodontic intervention, such as braces or aligners, may be necessary to correct the alignment of the teeth and jaws.
- Collaboration with Speech Therapists: If tongue thrusting is causing speech difficulties, association with a speech therapist may be beneficial. They can provide exercises and techniques to improve speech articulation and reduce tongue thrusting.
Early addressing tongue thrusting is crucial to prevent further dental misalignment.
Consulting with a dentist or orthodontist experienced in treating tongue thrusting can help determine the underlying causes and recommend appropriate interventions.
Through a combination of therapy, behavior modification, and orthodontic treatment, individuals can correct the effects of tongue thrusting, improve their dental alignment, and minimize the development of buck teeth.
Jaw misalignment
Jaw misalignment is another common factor that can contribute to the development of buck teeth.
A discrepancy between the upper and lower jaws can affect the positioning of the teeth and lead to the dental protrusion.
Here’s how jaw misalignment can influence the development of buck teeth:
- Overgrowth of Upper Jaw: If the upper jaw grows excessively or is positioned forward compared to the lower jaw, it can result in an overjet or overbite. This means that the upper front teeth protrude beyond the lower front teeth, creating the appearance of buck teeth.
- Undergrowth of Lower Jaw: Conversely, if the lower jaw is underdeveloped or set back concerning the upper jaw, it can also contribute to buck teeth. The lack of proper alignment and balance between the jaws can result in dental protrusion.
- Malocclusion: Jaw misalignment often leads to malocclusion, which refers to the improper alignment of the teeth when the jaws come together. Malocclusion can include Class II malocclusion (overbite) or Class III malocclusion (underbite), which can further contribute to buck teeth.
- Functional Imbalances: Jaw misalignment can cause functional imbalances in how the teeth come together and function during chewing and biting. This can put additional strain on the teeth, leading to misalignment and the development of buck teeth.
Addressing jaw misalignment is crucial in correcting buck teeth. Treatment options may include:
- Orthodontic Intervention: Braces, aligners, or other orthodontic appliances can guide the teeth into proper alignment. By applying controlled forces to the teeth, orthodontic treatment can help correct the positioning of the teeth and improve overall jaw alignment.
- Orthognathic Surgery: Orthognathic surgery may be necessary in more severe cases of jaw misalignment. This surgical procedure involves repositioning the jaws to achieve proper alignment and balance. It combined with orthodontic treatment for comprehensive correction of buck teeth.
- Functional Jaw Orthopedics: Functional appliances may sometimes modify the jaws’ growth and development. These appliances can help align the jaws and improve the overall bite relationship, reducing the severity of buck teeth.
A thorough evaluation by a dentist or orthodontist specializing in jaw misalignment is essential to determine the underlying causes and recommend the most appropriate treatment approach.
However, early intervention recommended to address jaw misalignment and prevent buck teeth and dental health complications.
Early tooth loss or delayed tooth eruption
Early tooth loss or delayed tooth eruption can contribute to the development of buck teeth. Here’s how these factors can influence dental alignment:
Premature Tooth Loss: When primary (baby) teeth are lost prematurely due to decay, injury, or extraction, it can disrupt the natural tooth eruption sequence.
The adjacent teeth may shift or drift into the space, causing a lack of proper space for the permanent teeth to erupt.
This can result in crowding and misalignment, including buck teeth.
Delayed Tooth Eruption: If permanent teeth experience delayed eruption, it can disrupt the timing and sequence of dental development.
Adjacent teeth may move into the space reserved for the erupting teeth, causing misalignment and dental protrusion.
Space Issues: Proper tooth alignment relies on having adequate space within the dental arch for all the teeth to fit harmoniously.
However, early tooth loss or delayed tooth eruption can create space-related problems, leading to overcrowding or irregular positioning of the teeth.
This can contribute to the development of buck teeth.
It’s important to address early tooth loss or delayed tooth eruption to minimize the risk of developing buck teeth. Treatment options may include:
Space Maintenance: If a primary tooth is lost prematurely, a space maintainer recommended to preserve the space until the permanent tooth erupts.
This prevents adjacent teeth from shifting and helps maintain proper alignment.
Orthodontic Intervention: Orthodontic treatment, such as braces or aligners, can correct misalignment caused by early tooth loss or delayed tooth eruption.
These appliances help guide the teeth into proper alignment and create sufficient space for erupting teeth.
Monitoring and Intervention: Regular dental check-ups and monitoring are essential to identify any developmental delays or concerns.
Early intervention can initiate to address any emerging issues and prevent further complications.
Individuals can reduce the risk of developing buck teeth and achieve proper dental alignment by addressing early tooth loss or delayed tooth eruption.
Seeking guidance from a dentist or orthodontist specializing in pediatric dentistry or orthodontics is vital to determine the most suitable treatment approach based on individual circumstances.
Trauma or injury
Trauma or injury to the mouth or jaw can contribute to the development of buck teeth. Here’s how trauma or injury can impact dental alignment:
- Displacement of Teeth: Trauma or injury to the mouth can cause the teeth to be pushed or knocked out of their normal position. This displacement can lead to misalignment, including buck teeth.
- Alveolar Bone Fracture: Fractures to the alveolar bone, which houses the teeth, can affect the stability and positioning of the teeth. If the supporting bone is damaged, it may result in changes to the alignment of the teeth, potentially leading to buck teeth.
- Tooth Loss: Severe trauma or injury can result in losing one or more teeth. Like early tooth loss, the absence of teeth can cause neighboring teeth to shift and create space-related problems, leading to misalignment and buck teeth.
- Jaw Misalignment: In cases of significant trauma or injury to the jaw, the alignment of the upper and lower jaws can be affected. This can result in an improper bite relationship and misalignment of the teeth, potentially contributing to buck teeth.
- Malocclusion: Trauma or injury can cause malocclusion, such as an overbite or underbite. These malocclusions can result in dental protrusion and the development of buck teeth.
Addressing trauma or injury-related issues that contribute to buck teeth may involve the following:
- Emergency Dental Care: Promptly seeking emergency dental care after trauma or injury is essential to assess and address any immediate concerns, such as tooth displacement or fractures.
- Orthodontic Intervention: Orthodontic treatment, such as braces or aligners, can help realign the teeth and correct any misalignment caused by trauma or injury. These appliances apply gentle forces to guide the teeth back into their proper position.
- Restorative Dentistry: If tooth loss occurs due to trauma or injury, therapeutic dental procedures like dental implants, bridges, or dentures recommended to replace the missing teeth and restore proper dental alignment.
- Jaw Reconstruction: In cases of severe jaw trauma or injury that significantly affects the alignment of the jaws, surgical jaw reconstruction may be necessary. This procedure aims to restore the proper position and alignment of the jaws, which can help address buck teeth caused by jaw misalignment.
Consulting with a dentist or orthodontist experienced in managing trauma-related dental issues is crucial for proper evaluation and personalized treatment planning.
Timely intervention can help correct the effects of trauma or injury, minimize the development of buck teeth, and restore oral health and function.
Effects of Buck Teeth
Aesthetics and self-esteem issues
Buck teeth can significantly impact a person’s aesthetics and self-esteem. The appearance of protruding or misaligned teeth may make individuals self-conscious about their smile and overall facial appearance. This can lead to a range of emotional and social challenges, including:
- Self-Consciousness: People with buck teeth may feel self-conscious about their smile and try hiding their teeth when speaking, laughing, or smiling. They may develop a habit of covering their mouth with their hand or avoiding situations that draw attention to their teeth.
- Teasing and Bullying: Unfortunately, individuals with noticeable dental protrusion are more susceptible to teasing, ridicule, and bullying, particularly during childhood and adolescence. Such adverse experiences can significantly impact their self-esteem and overall well-being.
- Social Withdrawal: The self-consciousness and fear of judgment associated with buck teeth can lead to social withdrawal. Individuals may avoid social situations, making it challenging to form connections and engage in activities that promote personal growth and social interaction.
- Negative Body Image: Buck teeth can contribute to a negative body image, as individuals may perceive their dental appearance as a flaw. This distorted self-perception can affect their overall self-esteem and confidence in various aspects of life.
Addressing buck teeth’ aesthetic and self-esteem issues is essential to comprehensive treatment.
Orthodontic interventions, such as braces or aligners, can help correct dental protrusion and improve teeth alignment, positively impacting facial aesthetics and boosting self-confidence.
In cases where the emotional impact is significant, additional support may be necessary, such as:
- Counseling or Therapy: Seeking the guidance of a mental health professional, such as a counselor or therapist, can help individuals address and overcome the emotional challenges associated with their appearance. Therapy can provide strategies to build self-esteem, develop coping mechanisms, and enhance overall well-being.
- Support Networks: Connecting with support networks, such as support groups or online communities, can be valuable. Sharing experiences, receiving encouragement, and finding a sense of belonging with others who have faced similar challenges can provide emotional support.
- Communication and Education: Discussing concerns with trusted family members, friends, or dental professionals can help individuals gain perspective and understanding. Education about the treatment options available and their positive impact on aesthetics and self-esteem can alleviate anxiety and promote acceptance.
It’s important to remember that addressing aesthetics and self-esteem issues related to buck teeth is not solely about cosmetic concerns.
It’s about supporting individuals in achieving a positive self-image, improved oral health, and overall psychological well-being.
By combining orthodontic treatment with emotional support, individuals can overcome the challenges associated with buck teeth and confidently embrace their unique smile.Top of Form
Difficulty in speaking and articulation
Buck’s teeth can sometimes cause difficulties in speaking and articulation.
The misalignment or protrusion of the front teeth can affect the proper positioning of the tongue, lips, and other oral structures involved in speech production.
Here’s how buck teeth can impact speech:
- Lisping: Lisping is an everyday speech issue associated with buck teeth. When the upper front teeth protrude significantly, it can interfere with the placement of the tongue during certain sounds, mainly “s” and “z” sounds. This can result in a distortion of these sounds and create a lisp.
- Dentalized Sounds: Buck teeth can cause certain sounds, such as “th” (as in “think” or “that”), to pronounce with decentralized or interdental production. The protrusion of the upper teeth may cause the tongue to contact the front teeth, affecting the proper sound production.
- Tongue Placement and Articulation: The misalignment of teeth can disrupt the natural positioning and movement of the tongue during speech. This can impact the clarity and precision of various sounds, making articulating words difficult.
- Overall Speech Intelligibility: In some cases, severe buck teeth or significant misalignment can impact public speech intelligibility. The altered oral structure and positioning can result in unclear or distorted speech sounds, affecting communication and understanding.
Addressing speech difficulties associated with buck teeth may involve a combination of orthodontic treatment and speech therapy. Here are potential approaches:
- Orthodontic Intervention: Correcting the alignment of the teeth through orthodontic treatment, such as braces or aligners, can improve tongue placement and create a more favorable oral environment for speech production. Proper alignment of the teeth can help reduce lisping and other speech distortions.
- Speech Therapy: Working with a speech-language pathologist (SLP) or speech therapist can be beneficial in addressing specific speech challenges related to buck teeth. The SLP will assess the individual’s speech patterns, identify areas of difficulty, and provide targeted exercises and techniques to improve articulation and clarity.
- Articulation Exercises: Speech therapy may include exercises focusing on tongue placement, strengthening oral muscles, and practicing correct articulation of specific sounds. These exercises help individuals develop good speech patterns and overcome difficulties associated with buck teeth.
- Collaborative Treatment: Collaboration between an orthodontist and a speech-language pathologist is often beneficial to ensure comprehensive care. The orthodontist can provide insights into the alignment and positioning of the teeth, while the SLP can address specific speech challenges and monitor progress throughout the treatment process.
Individuals with buck teeth can improve their speech clarity, articulation, and overall communication skills by addressing the underlying dental alignment and working on speech techniques.
Seeking professional guidance from orthodontic and speech therapy experts is essential for a comprehensive approach to addressing difficulties in speaking and pronunciation.
Chewing and eating problems
Buck’s teeth can sometimes lead to difficulties with chewing and eating. The misalignment or protrusion of the front teeth can affect the proper alignment of the jaws and how the teeth come together when biting and chewing. Here’s how buck teeth can impact chewing and eating:
- Poor Bite Alignment: Buck teeth can result in an improper bite alignment, such as an overjet or overbite. This means that the upper front teeth protrude beyond the lower front teeth, affecting the way the teeth fit together when chewing. This misalignment can make it challenging to bite and tear food correctly.
- Limited Food Options: Individuals with buck teeth may experience difficulty biting into certain foods, particularly harder or larger items. Their front teeth may not meet adequately, making it harder to grasp and break down food. As a result, they may avoid certain foods or struggle to eat them comfortably.
- Inefficient Chewing: The misalignment of teeth caused by buck teeth can impact chewing efficiency. The teeth may not come together optimally, leading to inadequate grinding and breakdown of food. This can make the chewing process longer and more laborious.
- Jaw Discomfort or Pain: Improper bite alignment and strain on the jaw joints due to buck teeth can cause discomfort or pain while chewing. This may further discourage individuals from enjoying certain foods or lead to avoiding meals altogether.
Addressing chewing and eating problems associated with buck teeth may involve a combination of orthodontic treatment and dental guidance. Here are potential approaches:
- Orthodontic Intervention: Orthodontic treatment, such as braces or aligners, can help correct the misalignment of teeth caused by buck teeth. Aligning the teeth properly can improve bite alignment, enhancing chewing efficiency.
- Dental Guidance: A dentist or orthodontist can guide proper chewing techniques and strategies. They may recommend specific methods to break down food effectively, such as cutting food into smaller pieces or using alternative chewing patterns.
- Nutritional Support: In cases where certain foods are challenging to eat, a nutritionist or dietitian can guide alternative food choices that are easier to manage with buck teeth. They can help ensure individuals maintain a balanced diet while accommodating their chewing limitations.
- Jaw Pain Management: If jaw discomfort or pain is present, the dentist or orthodontist can offer strategies to alleviate the symptoms. This may include recommending jaw exercises, using heat or cold therapy, or suggesting over-the-counter pain relievers for temporary relief.
By addressing the underlying misalignment of teeth and providing guidance on effective chewing techniques, individuals with buck teeth can improve their ability to chew and enjoy a broader range of foods.
Seeking professional advice from dental and orthodontic experts is crucial to developing an appropriate treatment plan and effectively addressing chewing and eating problems.
Increased risk of dental issues (e.g., cavities, gum disease)
Buck teeth can increase the risk of various dental problems. The misalignment or protrusion of the front teeth can affect oral health in several ways.
Here are some dental issues associated with buck teeth:
- Tooth Decay: Buck teeth can make cleaning and maintaining oral hygiene more difficult. The protrusion or misalignment of the front teeth can create areas that are challenging to reach with a toothbrush or floss. This increases the risk of plaque buildup, leading to tooth decay and cavities.
- Gum Disease: Inadequate oral hygiene due to the challenges of cleaning buck teeth can also contribute to gum disease. Plaque and bacteria can accumulate along the gumline, leading to inflammation and infection. If left untreated, gum disease can progress to more severe conditions, such as periodontitis, resulting in tooth loss.
- Tooth Wear: Buck teeth may experience excessive wear due to their position and alignment. The protruding front teeth may come into contact with opposing teeth abnormally during biting and chewing. This can lead to enamel erosion, tooth sensitivity, and an increased risk of fractures or chips.
- Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) Disorders: The misalignment of teeth caused by buck teeth can affect the proper functioning of the temporomandibular joint (TMJ). This can contribute to jaw pain, headaches, and TMJ disorders, which can cause discomfort and limited jaw movement.
- Speech Impairment: As mentioned earlier, buck teeth can impact speech and articulation. Difficulty with speech sounds can affect communication and lead to social and emotional challenges.
It’s essential to take proactive measures to mitigate the increased risk of dental issues associated with buck teeth,
- Oral Hygiene: Maintaining good oral hygiene is essential. Brushing two times daily with fluoride toothpaste, flossing daily, and using an antibacterial mouthwash can help reduce plaque buildup and the risk of tooth decay and gum disease.
- Regular Dental Check-ups: Routine dental check-ups and cleanings are essential for individuals with buck teeth. Dentists can monitor oral health, identify early signs of dental problems, and provide necessary treatments or interventions.
- Orthodontic Treatment: Correcting buck teeth through orthodontic treatment, such as braces or aligners, can improve alignment, making it easier to clean the teeth properly. This can reduce the risk of tooth decay, gum disease, and other dental issues associated with misalignment.
- Protective Measures: If excessive wear is a concern, a dentist may recommend using a mouthguard or other protective measures to minimize damage to the teeth.
By addressing the misalignment of buck teeth and maintaining good oral hygiene practices, individuals can reduce the risk of dental problems and maintain optimal oral health.
Regular dental care and professional guidance are essential for effectively preventing and treating dental issues associated with buck teeth.
Treatment Options for Buck Teeth
Orthodontic treatments
Braces
Braces are a standard orthodontic treatment for correcting dental misalignments, including buck teeth. They involve brackets, wires, and other components to move the teeth into their desired positions gradually. Here’s what you need to know about braces for addressing buck teeth:
- Evaluation and Treatment Planning: Before starting braces treatment, an orthodontist will conduct a thorough examination, which may include X-rays, photographs, and dental impressions. They will assess the severity of the buck teeth, evaluate the overall alignment of the teeth and jaws, and develop a personalized treatment plan.
- Braces Application: The braces application process typically begins with thorough teeth cleaning and preparation. The orthodontist will bond small brackets to the front surfaces of the teeth using a dental adhesive. These brackets act as anchors for the wires and other components.
- Archwire and Elastic Bands: After the brackets are in place, an archwire is threaded through them, connecting the brackets. The archwire applies gentle pressure to the teeth, gradually guiding them into their correct positions. Elastic bands used to help with specific tooth movements.
- Adjustments and Tightening: Periodic appointments are necessary throughout the braces treatment process. During these visits, the orthodontist will adjust and tighten the wires every few weeks to ensure consistent progress in realigning the teeth.
- Length of Treatment: The duration of braces treatment for buck teeth varies depending on the severity of the misalignment and individual factors. On average, braces worn for approximately 1 to 3 years; however, the actual time can be shorter or longer, depending on the case.
- Retainers: After removing the braces, a retainer typically provided to help maintain the newly achieved teeth alignment. They can be removable or fixed, and they are crucial for preventing teeth from shifting back to their original positions.
- Oral Hygiene and Care: Good oral hygiene is essential during braces treatment. It’s important to brush thoroughly, floss daily, and follow any specific oral care instructions the orthodontist provides. Regular dental check-ups are also necessary to monitor oral health throughout treatment.
Braces can effectively address buck teeth by gradually repositioning the teeth into proper alignment.
They provide precise control and allow for individualized adjustments to achieve optimal results.
However, it’s important to remember that each case is unique, and treatment plans may vary.
Consulting with an orthodontist is crucial to determine the most appropriate treatment approach for correcting buck teeth using braces.
They will assess your needs, explain the process, and guide you through the treatment journey.
Invisalign
Invisalign is an orthodontic treatment alternative to traditional braces for correcting dental misalignments, including buck teeth.
It utilizes a series of custom-made, clear, removable aligners to fit over your teeth. Here’s what you need to know about Invisalign for addressing buck teeth:
- Consultation and Treatment Planning: The Invisalign treatment process begins with a consultation with an orthodontist or dentist trained in Invisalign. They will evaluate your teeth, discuss your concerns, and determine if Invisalign is suitable for correcting your buck teeth.
- Digital Impressions and Treatment Simulation: To create customized Invisalign aligners, your orthodontist will take digital impressions of your teeth using a 3D scanning system. These impressions will create a digital treatment plan showing your teeth’ step-by-step movement throughout the treatment. You will also get a preview of what your final smile may look like.
- Custom Aligners: A series of clear aligners will be created specifically for you based on the treatment plan. Each set of aligners designed to shift your teeth into their proper positions gradually. You will typically wear each set of aligners for about one to two weeks before moving on to the next stage in the series.
- Removable and Virtually Invisible: One of the main advantages of Invisalign is that the aligners are virtually invisible when worn. They are made of clear, BPA-free plastic, making them less noticeable than traditional braces. Additionally, Invisalign aligners are removable, allowing you to take them out for eating, brushing, and flossing, making oral hygiene easier.
- Regular Check-ups: Throughout your Invisalign treatment, you will have regular check-ups with your orthodontist to monitor your progress. These appointments usually occur every few weeks, during which your orthodontist may provide you with new aligners to continue your treatment.
- Treatment Duration: Invisalign treatment for buck teeth varies depending on the severity of the misalignment and individual factors. In general, treatment times range from several months to over a year. Your orthodontist will provide a more accurate estimate based on your specific case.
- Retainers: Like with traditional braces, after completing Invisalign treatment, it is typically recommended to wear retainers to help maintain the alignment of your teeth. They can be removable or fixed, and they are crucial for preventing teeth from shifting back to their original positions.
Invisalign offers a discreet and convenient alternative to traditional braces for correcting buck teeth.
However, not everyone qualifies for Invisalign, as severe misalignments may require other orthodontic options.
Consulting with an Invisalign provider will help determine if this treatment suits your case.
They will guide you through the process, monitor your progress, and help you achieve the desired results in aligning your teeth.
Retainers
Retainers are dental appliances used after orthodontic treatment, including braces or Invisalign, to help maintain the newly achieved teeth alignment.
They are crucial in preventing the teeth from returning to their original positions. Here’s what you need to know about retainers:
Types of Retainers: There are two main types of retainers:
- Removable Retainers: These retainers typically made of clear plastic or acrylic material. They fit over the teeth and are easily removable for eating, brushing, and flossing. Removable retainers are convenient but require consistent wear as prescribed by your orthodontist.
- Fixed Retainers: Fixed or bonded retainers are thin wires attached to the front teeth’ back surfaces using dental cement. Fixed retainers used for the lower front teeth but can also be used on the upper teeth.
Retention Period: The duration of retainer wear varies depending on the individual case. Generally, it is recommended to wear retainers full-time immediately after orthodontic treatment for a certain period, usually a few months.
After the initial full-time wear, the orthodontist may transition you to wearing retainers only at night.
However, your orthodontist determines the duration and instructions for retainer wear based on your circumstances.
Importance of Retainers: Teeth naturally shift and move even after orthodontic treatment, known as orthodontic relapse.
Retainers help prevent this relapse by maintaining the corrected positions of the teeth while the surrounding supportive structures, such as the gums and bone, adapt to the new alignment.
Regular and consistent retainer wear is crucial to ensure the stability of your orthodontic results.
Care and Maintenance: Proper care and safeguarding retainers are essential for their effectiveness and longevity. Here are some general guidelines:
- Cleanliness: Removable retainers should use a soft toothbrush and mild soap or non-abrasive denture cleaner daily. Avoid using hot water, as it can distort the retainer. Fixed retainers require regular brushing and flossing around the wires to remove plaque and food particles.
- Storage: When not in use, removable retainers should store in their provided cases to protect them from damage or loss. Avoid wrapping them in tissues or napkins, as they can easily discard accidentally.
- Follow Instructions: Follow your orthodontist’s instructions regarding retainer wear and maintenance. Attend regular check-ups to ensure the retainers fit correctly and to address any concerns or issues.
- Replacement and Repair: Retainers may need to be replaced or repaired over time due to normal wear and tear or accidental damage.
If your retainer becomes damaged or no longer fits properly, contact your orthodontist for evaluation and necessary adjustments or replacements.
Remember, the proper use of retainers is essential for maintaining the results of your orthodontic treatment.
Follow your orthodontist’s instructions carefully, wear your retainers as directed, and attend regular check-ups to ensure long-term stability and oral health.
Dental appliances
Headgear
Headgear is an orthodontic appliance that is sometimes combined with braces to correct certain types of dental and jaw misalignments.
An external metal frame or wire attaches to braces or other dental appliances inside the mouth. Here’s what you need to know about headgear:
Purpose: Headgear primarily used to exert pressure on the upper jaw or teeth to promote proper alignment and growth.
It can help address various orthodontic issues, including overbites (protrusion of upper teeth), underbites (protrusion of lower teeth), and excessive spacing or crowding of teeth.
Headgear typically consists of the following components:
Facebow:
This metal bar attaches to the braces or other dental appliances inside the mouth, extends outside the mouth, and connects to the headgear frame.
Headgear Frame:
The frame is worn outside the mouth and rests against the back of the head or neck. It provides support and stability for the facebow.
Straps or Bands:
Straps or bands are used to secure the headgear frame to the head or neck. They are adjustable to ensure a proper fit and provide the necessary force to move the teeth or jaw.
Types of Headgear:
There are different types of headgear used based on the specific orthodontic needs:
Cervical-Pull Headgear:
This type of headgear attaches to the back of the upper teeth and pulls the upper jaw backward to correct overbites.
High-Pull Headgear:
High-pull headgear connects to the braces on the upper teeth and applies force to the upper jaw and upper teeth, helping correct overbites and encourage proper jaw growth.
Reverse-Pull or Delaire Headgear:
Reverse-pull headgear correct underbites by applying forward pressure to the upper jaw or teeth, encouraging proper alignment and growth.
Duration of Wear:
The amount of time headgear worn daily varies depending on the orthodontic condition and treatment plan.
Your orthodontist will provide instructions on the duration and frequency of headgear wear.
Typically, it recommended to wear headgear for a certain number of hours per day, usually during evenings and overnight while sleeping.
Compliance and Adjustments:
Consistent and proper use of headgear is essential for effective treatment.
Following your orthodontist’s instructions regarding wearing schedules and care is critical.
Regular adjustments and check-ups with your orthodontist are necessary to monitor progress, adjust the headgear, and assess the overall treatment plan.
Side Effects and Discomfort:
Initially, wearing headgear may feel uncomfortable, and there may be some pressure or soreness in the mouth, teeth, or jaw.
However, these discomforts typically subside as you get accustomed to wearing the appliance.
It’s essential to communicate any significant pain or concerns to your orthodontist.
Headgear is a specialized orthodontic appliance that, when used as part of a comprehensive treatment plan, can help address specific dental and jaw alignment issues.
It is essential to check with an experienced orthodontist who will evaluate your particular needs and determine if headgear is necessary as part of your orthodontic treatment.
They will provide detailed instructions on its use, monitor your progress, and make any adjustments or modifications to ensure effective results.
Palatal expanders
Palatal, orthodontic, or rapid maxillary expanders are dental appliances that widen the upper jaw (maxilla) and correct dental and skeletal development issues.
Here’s what you need to know about palatal expanders:
Purpose:
Palatal expanders primarily address crossbites, crowded teeth, narrow dental arches, and other conditions resulting from a narrow upper jaw.
By gradually expanding the palate, the appliance creates more space for the teeth to align correctly and can also help improve breathing and nasal airflow.
Construction:
Palatal expanders have an expansion screw or mechanism attached to a metal framework.
The framework is custom-made to fit the roof of the mouth (palate) and secured to the back teeth with bands or rings.
Activation and Expansion:
According to the orthodontist’s instructions, the palatal expander activated by turning the expansion screw.
This gradually widens the appliance and applies gentle, controlled pressure on the bones of the palate, encouraging them to separate and create additional space.
Adjustment Period: Initially, patients may experience a feeling of pressure or tension in the palate during the expansion process.
However, this discomfort is usually mild and temporary. Following the orthodontist’s instructions for turning the expander to achieve the desired expansion is essential.
Active and Retention Phase:
The active phase of palatal expansion typically lasts a few weeks to a few months, depending on the specific case and treatment plan.
Once the desired growth achieved, the appliance is usually left in place to stabilize the newly created space and the surrounding tissues to adapt.
This retention phase helps prevent relapse and ensures the long-term stability of the expansion.
Hygiene and Care:
Proper oral hygiene during palatal expander treatment is crucial.
Brushing the expander, the roof of the mouth, and teeth thoroughly is essential to prevent plaque buildup.
Particular attention given to cleaning around the bands or rings and the expansion screw. Your orthodontist will provide specific instructions on cleaning techniques and oral care practices.
Follow-up and Monitoring:
Regular visits to the orthodontist are necessary throughout the palatal expansion process.
These appointments allow the orthodontist to monitor progress, make necessary adjustments to the expander, and ensure the treatment progresses as planned.
Palatal expanders are effective orthodontic appliances for widening the upper jaw and creating space for proper dental alignment.
The treatment is typically recommended during childhood or early adolescence when the jaw bones are still growing and more responsive to expansion.
Consulting with an experienced orthodontist is essential to determine if palatal expansion is appropriate for your case.
They will thoroughly examine your dental and skeletal condition and develop a personalized treatment plan to address your needs.
Surgical interventions
Tooth extraction
Tooth extraction is a dental procedure removing a tooth from its jawbone socket.
It’s done for various reasons like severe decay, impacted wisdom teeth, crowding, infection, or trauma.
The dentist numbs the area, loosens the tooth, and removes it using forceps or surgery. Afterward, a blood clot forms and the patient receives instructions for post-extraction care.
Jaw surgery
Jaw surgery, also known as orthognathic surgery, is a procedure that involves correcting irregularities or abnormalities in the jaw.
It performed to improve jaw function, bite alignment, facial aesthetics, and overall oral health.
The surgery may involve repositioning the upper jaw, lower jaw, or both and can address issues such as overbite, underbite, open bite, or facial asymmetry.
It is typically performed by an oral and maxillofacial surgeon in a hospital setting under general anesthesia.
Recovery time can vary depending on the extent of the surgery, and post-operative care is crucial for optimal healing and results.
Prevention and Management of Buck Teeth
Early intervention
Early intervention refers to timely and proactive support for individuals experiencing developmental delays or disabilities.
It involves identifying and addressing concerns in a person’s development as early as possible to minimize the impact on their overall growth and well-being.
Early intervention programs typically focus on providing specialized services, therapies, and resources tailored to the specific needs of the individual.
The goal is to optimize their development, enhance their abilities, and promote their overall quality of life.
Breaking a thumb-sucking habit
Breaking a thumb-sucking habit involves stopping placing the thumb in the mouth for comfort or soothing purposes.
Various strategies can use to discourage thumb-sucking, such as positive reinforcement, offering alternatives, applying bitter-tasting substances to the thumb, or using devices like thumb guards.
The aim is to help individuals overcome the habit and promote healthy oral development.
Tongue exercises and therapy
Tongue exercises and therapy involve specific movements and activities to improve the tongue’s strength, coordination, and function.
These exercises designed to address issues such as speech difficulties, swallowing problems, or oral motor disorders.
They may include activities like tongue stretches, tongue lifts, and tongue lateralization.
Tongue therapy aims to enhance tongue muscle control and improve oral motor skills for improved speech and swallowing abilities.
Regular dental check-ups
Regular dental check-ups involve routine visits to the dentist for preventive care and oral health monitoring.
These check-ups include examinations of the teeth, gums, and mouth to identify any issues or potential problems early on.
The dentist may perform professional cleanings, check for cavities, assess gum health, and take X-rays if necessary.
Usual dental check-ups are essential for maintaining oral hygiene, preventing dental problems, and promptly addressing concerns.
Oral hygiene practices
Oral hygiene practices refer to routines and habits that promote good oral health.
These practices include brushing teeth, flossing, and using mouthwash regularly.
Brushing removes plaque and bacteria from the teeth and gums, while flossing helps clean between the teeth and along the gum line.
Mouthwash can provide additional benefits, such as freshening breath and reducing bacteria.
Good oral hygiene prevents gum disease and tooth decay and maintains a healthy smile.
Psychological and Emotional Support
Counseling and therapy
Counseling and therapy involve professional support and guidance to address personal, emotional, or psychological challenges.
Through counseling and treatment, individuals can explore their thoughts, feelings, and behaviors, gain insights into their concerns, and develop coping strategies.
Therapists provide a safe and private space to express themselves, navigate life’s difficulties, and work toward personal growth and well-being.
Counseling and therapy can help improve mental health, enhance relationships, and promote overall emotional wellness.
Support groups and peer networks
Support groups and peer networks provide an inclusive environment where individuals with similar experiences or challenges come together to share and exchange support.
These groups offer a sense of belonging, understanding, and empathy as members can relate to one another’s struggles.
Support groups and peer networks foster mutual encouragement, shared knowledge, and practical advice to help individuals cope with their situations.
They can benefit individuals facing addiction, chronic illness, grief, or mental health concerns.
Being part of a support group or peer network can provide comfort, validation, and a valuable sense of community.
Building self-confidence and self-acceptance
Building self-confidence and self-acceptance involves developing a positive and healthy relationship with oneself.
It includes recognizing and appreciating one’s strengths, abilities, and unique qualities while accepting and embracing personal flaws and imperfections.
Building self-confidence and self-acceptance can be achieved through various practices such as setting realistic goals, practicing self-care and self-compassion, challenging negative self-talk, surrounding oneself with supportive and uplifting people, and engaging in activities that promote personal growth and self-expression.
By nurturing self-confidence and self-acceptance, individuals can enhance their well-being, improve relationships, and approach life with greater fulfillment and resilience.
Conclusion
Recap of the importance of addressing buck teeth
Addressing buck teeth is vital for several reasons. Buck teeth, also known as protruding front teeth, can affect a person’s appearance, self-esteem, and oral health.
Protruding teeth are more vulnerable to trauma and injury. They can also make it challenging to maintain proper oral hygiene, increasing the risk of tooth decay and gum disease.
Individuals can improve their smile, enhance oral health, and boost self-confidence by addressing buck teeth through orthodontic treatment, such as braces or aligners.
Seeking professional help is essential for addressing personal challenges. Professionals offer expertise, support, and guidance to help individuals navigate their difficulties effectively.